My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine 2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head
Head- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
4 Cylinder Heads found
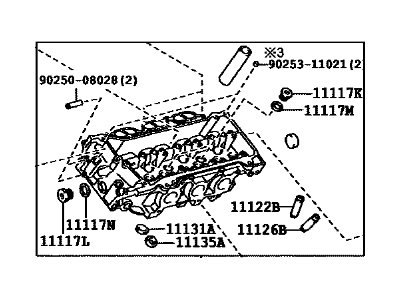
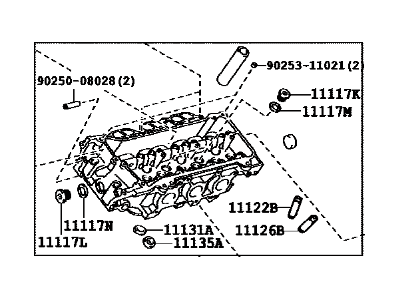
2009 Toyota Sienna Head Sub-Assembly, Cylinder, Driver Side
Part Number: 11102-39055$1211.64 MSRP: $1538.58You Save: $326.94 (22%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Head, Cylinder, LH
- Position: Driver Side
- Replaced by: 11102-09142
- Part Name Code: 11102
- Item Weight: 26.80 Pounds
- Item Dimensions: 22.6 x 12.3 x 10.9 inches
- Condition: New
- Fitment Type: Direct Replacement
- SKU: 11102-39055
- Warranty: This genuine part is guaranteed by Toyota's factory warranty.
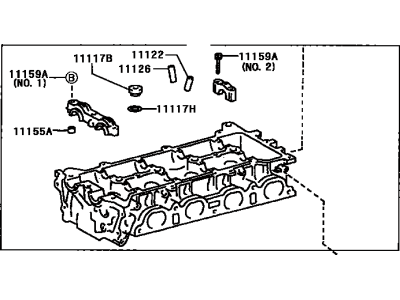
2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head Sub-Assembly
Part Number: 11101-09260$1212.99 MSRP: $1540.30You Save: $327.31 (22%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Head Sub-Assy, Cylinder
- Replaced by: 11101-09262
- Part Name Code: 11101
- Item Weight: 28.10 Pounds
- Item Dimensions: 22.2 x 13.4 x 10.5 inches
- Condition: New
- Fitment Type: Direct Replacement
- SKU: 11101-09260
- Warranty: This genuine part is guaranteed by Toyota's factory warranty.
2009 Toyota Sienna Head, Cylinder, LH
Part Number: 11102-09140$1211.64 MSRP: $1538.58You Save: $326.94 (22%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Position: Driver Side
- Replaced by: 11102-09142
- Part Name Code: 11102
- Item Weight: 27.80 Pounds
- Item Dimensions: 21.9 x 12.7 x 10.6 inches
- Condition: New
- Fitment Type: Direct Replacement
- SKU: 11102-09140
- Warranty: This genuine part is guaranteed by Toyota's factory warranty.
2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head Sub-Assembly
Part Number: 11101-39535$1212.99 MSRP: $1540.30You Save: $327.31 (22%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Head Sub-Assy, Cylinder
- Replaced by: 11101-09262
- Part Name Code: 11101
- Item Weight: 26.60 Pounds
- Item Dimensions: 23.2 x 13.1 x 10.8 inches
- Condition: New
- Fitment Type: Direct Replacement
- SKU: 11101-39535
- Warranty: This genuine part is guaranteed by Toyota's factory warranty.
2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head
With ToyotaPartsDeal.com, you have access to an extensive inventory of genuine 2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head, all priced competitively. Feel secure in your purchase, as all our OEM 2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head are covered by the manufacturer's warranty. Plus, we offer a hassle-free return policy and speedy delivery service.
2009 Toyota Sienna Cylinder Head Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to clean and inspect cylinder heads and valve components during an engine overhaul for the 2009 Toyota Sienna?A: It is also necessary to clean the cylinder head(s) and other parts that are associated with the valve train before assessing all the service work that is required to overhauled the valves. Remove all old gasket material and compound residues from the head gasket, intake manifold/gasket, and exhaust manifold/gasket surfaces, but do not cut or damage the cylinder head. Scrub off any the scale deposit on the coolant passages clean and also use a hard wire brush to clean up the deposit on several holes. Apply an appropriate size of tap to clear the holes of corrosion and thread sealant, additionally, compressed air can be used to blow debris. Finally, clean threads of the exhaust and intake manifold stud with wire brush; clean the cylinder head with solvent, and then use the air pressure to rinse it properly. After that, remove the lifters from the engine and clean them with solvent and dry it and if they have to be stored, do not mix them with others, the same is applicable to the valve springs, spring seat, keepers, and retainers, the auto mechanic or the technician should clean them one at a time. Strip thick accumulation off the valve faces and apply motorized wire wheel for the valve head and stem while preserving the valves separate. Spray the head with water and visually look for cracks, leakage signs, or any other signs of damages and take it for repairs from an automotive machine shop. Visually inspect the head gasket mating surface for warpage with the straightedge and feeler gauge and if it warpage is tat is above the limit then the surafcing can be done at a maching shop. Valve seats are to be inspected for any signs of pitting, cracking or signs of burning while the valve stem-to-guide clearance coupled with deflection has to be tested and measured with a dial indicator and valve guides have to be replaced if the clearance exceed the limit. Every single valve face must be examined for wear, deformation as well as cracks, the margin width must be measured, as there will be need to replace the valve once the width of the margin is small. Looking at each valve spring, measure the free length against specification, and remove any that are shorter or sagged, and pressure check the tension of all the springs before reusing them. Once a year stand each spring on a flat surface to make sure the spring is square and replace any noticeably distorted or sagged springs In addition, inspect the springs retainers and keepers for wear and cracks and replace any questionable items. Last but not the least, if, based on the inspection, the components of the valves are poor and beyond the wear limit, assemble the valves in the cylinder head again.