My Garage
My Account
Cart
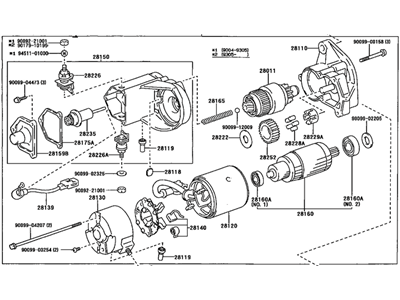
Genuine Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Motor
Starter Ignition- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
18 Starter motors found
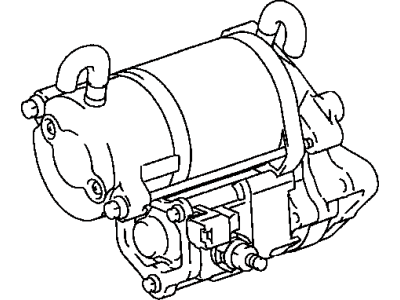
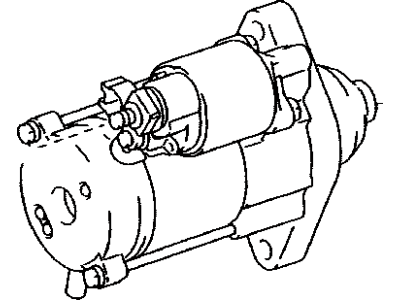
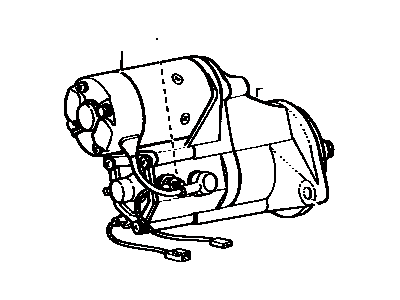
Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-66060$163.69 MSRP: $231.38You Save: $67.69 (30%)Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Motor
Part Number: 28100-50101$140.28 MSRP: $198.03You Save: $57.75 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-66040$167.28 MSRP: $236.49You Save: $69.21 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-50100$116.90 MSRP: $163.33You Save: $46.43 (29%)Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-66050$163.69 MSRP: $231.38You Save: $67.69 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-50070$116.90 MSRP: $163.33You Save: $46.43 (29%)Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-60061$114.09 MSRP: $159.37You Save: $45.28 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-60042$208.59 MSRP: $302.20You Save: $93.61 (31%)Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-60041$114.09 MSRP: $159.37You Save: $45.28 (29%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-38040$212.85 MSRP: $305.21You Save: $92.36 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-38041$212.85 MSRP: $305.21You Save: $92.36 (31%)Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-60040$216.39 MSRP: $310.28You Save: $93.89 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Land Cruiser Starter Assembly
Part Number: 28100-38080$212.85 MSRP: $305.21You Save: $92.36 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Motor
The Starter Motor Motor used in Toyota Land Cruiser automobiles serves the function of converting electrical energy from the battery into mechanical energy needed in cranking the engine. It functions through an externally positioned solenoid which is connected to the battery, it energises the starter motor. In starter, a rotating armature cooperates with field coils or permanent magnets to develop the degree of torque to mesh the starter's drive with the engine's flywheel. Several years on the market, different kinds of starters were applied in the Land Cruiser, including the gear reduction starters that increase the efficiency of the device, using the reduction gear for the drive. In general, starters used for OE are the ones that fit standard engines and where high performance vehicles are a concern, then likely to require high compression motors, a high performance starter is useful. Such developments in the starter technologies make for proper engine startups in the various models of the Land Cruiser range.
If you are in demand for superior quality and affordable OEM Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Motor, then shop with us! We own a wide range of the reduced-priced genuine Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Motor. You can purchase in confidence as all parts come with a manufacturer's warranty. Any issues with our products? No need to worry as we have a hassle-free return policy to guide you every step of the way.
Toyota Land Cruiser Starter Motor Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to Diagnose Starter Motor Problems on Toyota Land Cruiser?A:Before diagnosing starter issues, ensure the Car Batteries is fully charged. Check if the starter motor turns when the switch is operated. Verify clean and secure cables at battery and Starter Solenoid terminals. If the motor spins but the engine doesn't crank, replace the starter motor due to a slipping over-running clutch. If the solenoid clicks but the motor doesn't operate, investigate battery, solenoid contacts, starter motor, or a seized engine as possible causes. If no solenoid sound is heard, check battery, fusible link, starter relay, or solenoid. Test the solenoid with a jumper lead. If the starter motor works, the solenoid is fine, else investigate the ignition switch, Neutral start switch, or wiring. If the motor cranks abnormally slowly, confirm charged battery and tight connections. A partially seized engine or wrong viscosity oil can cause slow cranking. Perform voltage tests during cranking. A reading of nine volts or more at normal cranking speed is normal. Less than nine volts with slow cranking indicates possible issues with solenoid contacts, starter motor, battery, or connections.
Related Toyota Land Cruiser Parts
Browse by Year
2021 Starter Motor 2020 Starter Motor 2019 Starter Motor 2018 Starter Motor 2017 Starter Motor 2016 Starter Motor 2015 Starter Motor 2014 Starter Motor 2013 Starter Motor 2012 Starter Motor 2011 Starter Motor 2010 Starter Motor 2009 Starter Motor 2008 Starter Motor 2007 Starter Motor 2006 Starter Motor 2005 Starter Motor 2004 Starter Motor 2003 Starter Motor 2002 Starter Motor 2001 Starter Motor 2000 Starter Motor 1999 Starter Motor 1998 Starter Motor 1997 Starter Motor 1996 Starter Motor 1995 Starter Motor 1994 Starter Motor 1993 Starter Motor 1992 Starter Motor 1991 Starter Motor 1990 Starter Motor 1989 Starter Motor 1988 Starter Motor 1987 Starter Motor 1986 Starter Motor 1985 Starter Motor 1984 Starter Motor 1983 Starter Motor 1982 Starter Motor 1981 Starter Motor 1980 Starter Motor 1979 Starter Motor 1978 Starter Motor 1977 Starter Motor 1976 Starter Motor 1975 Starter Motor 1974 Starter Motor 1973 Starter Motor 1972 Starter Motor 1971 Starter Motor 1970 Starter Motor 1969 Starter Motor