My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Toyota Tercel Carburetor
Engine Carburetor, Carb- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
45 Carburetors found
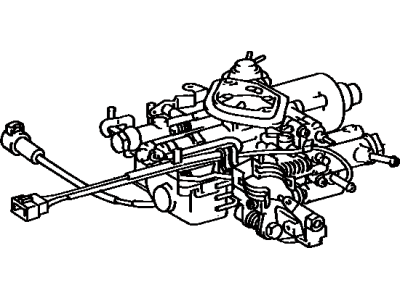
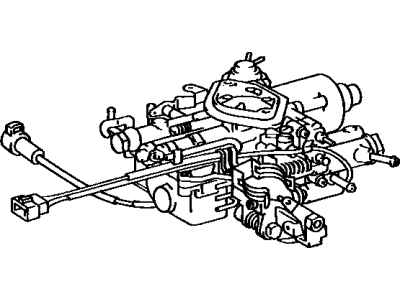
Toyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-11400$328.37 MSRP: $475.72You Save: $147.35 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Kit, High Altitude, Performance, Modification
Part Number: 04214-15020$31.51 MSRP: $44.05You Save: $12.54 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15101$693.78 MSRP: $1046.58You Save: $352.80 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15120$731.26 MSRP: $1091.88You Save: $360.62 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel CARBURETOR Kit
Part Number: 04211-15062$47.40 MSRP: $66.24You Save: $18.84 (29%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15130$413.20 MSRP: $529.46You Save: $116.26 (22%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15080$197.41 MSRP: $242.95You Save: $45.54 (19%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15100$237.94 MSRP: $292.84You Save: $54.90 (19%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15140$237.94 MSRP: $292.84You Save: $54.90 (19%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-15150$237.94 MSRP: $292.84You Save: $54.90 (19%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Carburetor Assembly
Part Number: 21100-11430$239.45 MSRP: $294.93You Save: $55.48 (19%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
| Page 1 of 3 |Next >
1-20 of 45 Results
Toyota Tercel Carburetor
If you are in demand for superior quality and affordable OEM Toyota Tercel Carburetor, then shop with us! We own a wide range of the reduced-priced genuine Toyota Tercel Carburetor. You can purchase in confidence as all parts come with a manufacturer's warranty. Any issues with our products? No need to worry as we have a hassle-free return policy to guide you every step of the way.
Toyota Tercel Carburetor Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: What are the important considerations before conducting major carburetor service work on Toyota Tercel?A:Before conducting major carburetor service work, it is important to perform a thorough road test and check carburetor adjustments. Carburetor problems can cause flooding, hard starting, stalling, severe backfiring, and poor acceleration. If the carburetor is leaking fuel or covered in wet deposits, it needs attention. However, performance complaints attributed to the carburetor may actually be caused by loose or malfunctioning engine or electrical components, vacuum hose leaks, or incorrect routing. A comprehensive analysis of carburetor problems should include inspecting vacuum hoses and actuators, tightening intake manifold and carburetor mounting nuts/bolts, performing a compression test, cleaning or replacing spark plugs, checking ignition components, inspecting timing, examining the Fuel Pump, assessing the air cleaner's heater control valve, checking/replacing the air filter, inspecting the PCV system, checking/replacing the fuel filter, examining the exhaust system, checking EGR valve operation, ensuring the choke is open at normal temperature, checking for fuel leaks and damaged fuel lines, inspecting accelerator pump operation, checking fuel quality, checking valve clearances and camshaft lift, and having a professional assess electronic controls. When diagnosing carburetor problems, running the engine without the air cleaner may be necessary but can lead to backfires. Overhauling the carburetor can be done with a rebuild kit and solvent or by obtaining a new or rebuilt carburetor. Follow the specific instructions provided with the overhaul kit, as carburetor designs vary.
- Q: How to remove the carburetor on Toyota Tercel?A:To remove the carburetor, start by relieving the tank pressure by removing the fuel tank cap. Then, remove the air cleaner from the carburetor and label all vacuum hoses attached to it. Disconnect the throttle cable and, if applicable, the Throttle Valve (TV) cable. Label and disconnect all vacuum hoses and fittings, as well as the fuel line from the carburetor. Label and unplug the electrical connectors attached to the carburetor. Remove the mounting fasteners, EGR modulator bracket, and lift the carburetor from the intake manifold, making sure not to remove the cold mixture heater. Stuff a shop rag into the intake manifold openings. To install, use a gasket scraper to remove any gasket material and sealant from the cold mixture heater and carburetor (if being reinstalled). Clean the mating surfaces with lacquer thinner or acetone. Place a new gasket on the cold mixture heater and position the carburetor on it. Attach the EGR modulator bracket and install the mounting fasteners, tightening them in a criss-cross pattern. The remaining steps are the reverse of removal. Finally, check and adjust the idle speed if necessary, and start the engine to check for fuel leaks.