My Garage
My Account
Cart
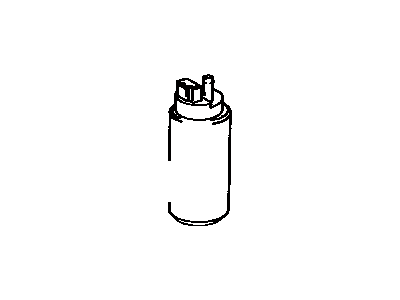
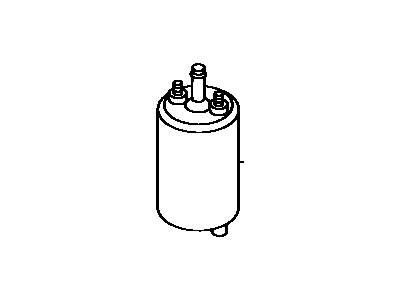
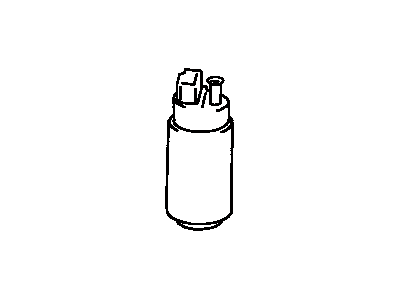
Genuine Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump
Gas Pump- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
7 Fuel Pumps found
Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23221-46010$273.63 MSRP: $392.37You Save: $118.74 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysToyota Tercel Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23220-43070$365.26 MSRP: $544.90You Save: $179.64 (33%)Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23221-11050$346.31 MSRP: $516.62You Save: $170.31 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business Days
Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump
If you are in demand for superior quality and affordable OEM Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump, then shop with us! We own a wide range of the reduced-priced genuine Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump. You can purchase in confidence as all parts come with a manufacturer's warranty. Any issues with our products? No need to worry as we have a hassle-free return policy to guide you every step of the way.
Toyota Tercel Fuel Pump Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to check the fuel pump on Toyota Tercel?A:To check the fuel system, start by ensuring there is enough fuel in the Fuel Tank. If there are doubts about the fuel gauge reading, a long wooden dowel can be inserted into the fuel filler opening to serve as a dipstick. For carbureted engines with a mechanical pump, raise the vehicle and inspect all fuel lines for leaks, loose connections, or kinks. Start the engine and check for leaks on the fuel pump. If there is little or no gasoline coming from the fuel line during engine cranking, the fuel line may be clogged or the fuel pump may need to be replaced. For fuel-injected engines with an electric pump, perform a fuel pump operation check by bridging terminals +B and Fp of the check connector to activate the fuel pump. Listen for fuel return noises and check for pressure in the hose from the fuel filter. If there is no pressure, inspect the electrical components such as fuses, relays, wiring, and connectors. To check the fuel pressure, a fuel pressure gauge with a banjo fitting is required. Attach the gauge and measure the fuel pressure, comparing it to the specifications. If the pressure is not as specified, check for restricted fuel return lines or replace the pressure regulator. Finally, check the fuel pump electrical components by testing for battery voltage to the relays and the fuel pump itself. If there is voltage present, have the relays checked by a professional. Additionally, check the fuel pressure regulator components by applying vacuum and comparing the fuel pressure readings. If the pressure is too high or low, replace the fuel pressure regulator. Lastly, test the fuel pressure control system by checking the resistance of the vacuum switching valve and ensuring proper airflow. Replace any faulty components as needed.