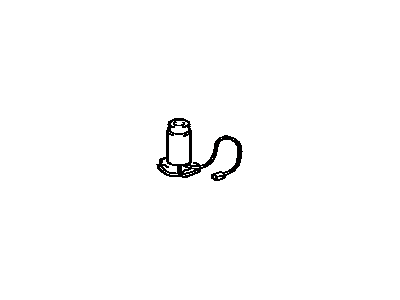My Garage
My Account
Cart
Genuine Toyota Fuel Pump
Gas Pump- Select Vehicle by Model
- Select Vehicle by VIN
Select Vehicle by Model
orMake
Model
Year
Select Vehicle by VIN
For the most accurate results, select vehicle by your VIN (Vehicle Identification Number).
321 Fuel Pumps found
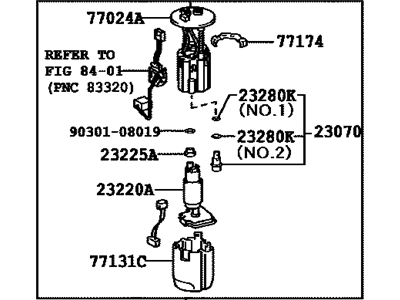
Toyota Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23221-46010$273.63 MSRP: $392.37You Save: $118.74 (31%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-04061$399.94 MSRP: $596.63You Save: $196.69 (33%)Product Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assy, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump, Fuel Pump Assembly
- Replaces: 77020-04060
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-0C082$399.27 MSRP: $595.63You Save: $196.36 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assembly, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump, Fuel Pump Assembly
- Replaces: 77020-0C081, 77020-0C080
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-35151$458.81 MSRP: $684.46You Save: $225.65 (33%)Product Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assembly, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump Assembly
- Replaces: 77020-35150
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-04090$448.44 MSRP: $668.99You Save: $220.55 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assembly, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump, Fuel Pump Assembly
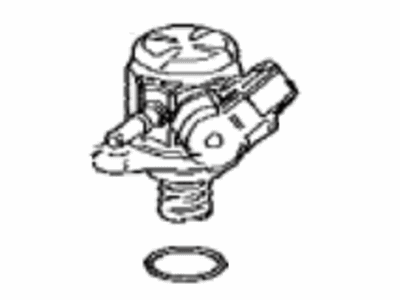
Toyota Mechanical Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23101-0P020$888.40 MSRP: $1326.51You Save: $438.11 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Sub-Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
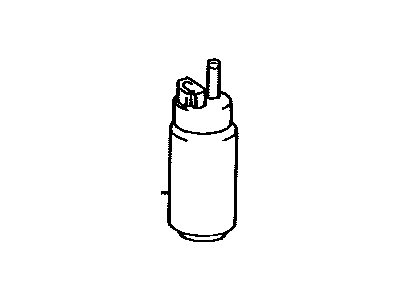
Toyota Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23100-61070$142.49 MSRP: $202.58You Save: $60.09 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
- Product Specifications
- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
- Product Specifications
- Other Name: Pump, Fuel
- Replaces: 23221-03040
Toyota Fuel Pump
Part Number: 23221-25030$122.69 MSRP: $174.41You Save: $51.72 (30%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump, Fuel; Fuel Pump Assembly, Pump
Toyota Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23100-39336$107.49 MSRP: $151.52You Save: $44.03 (30%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
- Replaces: 23100-39335
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-0C090$494.83 MSRP: $738.19You Save: $243.36 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assembly, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump, Fuel Pump Assembly
Toyota Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23220-16190$322.58 MSRP: $462.56You Save: $139.98 (31%)Ships in 1 Business DayProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-06286$451.45 MSRP: $673.48You Save: $222.03 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assembly, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump, Fuel Pump Assembly
- Replaces: 77020-06282, 77020-06285
Toyota Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23221-46060$364.82 MSRP: $544.23You Save: $179.41 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel
- Replaced by: 23221-66040
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-35121$504.86 MSRP: $753.15You Save: $248.29 (33%)Ships in 1-2 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assy, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump Assembly
- Replaces: 77020-35120
Toyota Fuel Pump Assembly
Part Number: 23221-74110$364.82 MSRP: $544.23You Save: $179.41 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Assembly, Fuel
- Replaced by: 23221-66040
Toyota Fuel Pump
Part Number: 23220-21132$357.01 MSRP: $532.59You Save: $175.58 (33%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump, Fuel
- Replaces: 23220-21131
Toyota Fuel Pump Sub-Assembly
Part Number: 23101-F0010$888.40 MSRP: $1326.51You Save: $438.11 (34%)Ships in 1-3 Business DaysProduct Specifications- Other Name: Pump Sub-Assembly, Fuel; Fuel Pump
- Replaces: 23101-25040
Toyota Fuel Suction Tube Assembly with Pump & Gage
Part Number: 77020-0C120$504.64 MSRP: $752.82You Save: $248.18 (33%)Product Specifications- Other Name: Tube Assembly, Fuel Suction W/Pump & Gage; Fuel Pump, Fuel Pump Assembly
| Page 1 of 17 |Next >
1-20 of 321 Results
About Toyota Fuel Pump
The Toyota fuel pump is responsible for delivering fuel to the fuel rail of your vehicle. All electric fuel pumps operate on current from the vehicles battery or charging system to move fuel as determined by load. When your fuel pump is operating properly in your vehicle, it will be delivering the required amounts of fuel as determined by the computer monitored load. If your vehicle runs completely out of gas often, the fuel pump in your vehicle may expire prematurely from being overworked and overheated.
Most fuel pump replacement involves dropping of the fuel tank, removal and disposal of gasoline, and cleaning of the tank. The cleaning of the tank is crucial so that no additional contaminants are present after the new part has been replaced. It is not uncommon for the moderate DIY mechanic to tackle the task of fuel pump replacement. A failing fuel pump may simply start with a rough starting vehicle, and can lead to you being stranded when you least expect it. There are voltage tests and pressure tests that can be performed on your vehicle to determine if your fuel pump has failed, or is in danger of failing in the near future.
ToyotaPartsDeal.com is a container for extensive collection of genuine OEM Toyota parts. The fuel pump you purchase here will fit your Toyota perfectly. We remove all concerns and anxieties about verifying the part from you, and there are professional part specialists ready to assist you with it. We will never disappoint you with the deeply discounted price, and we are proud that we make you happy. We understand that every customer wants to get the order as soon as possible, so we speed up the process time. The fuel pump will be delivered to you in a complete shape, and make your Toyota being a master again on the road.
Most fuel pump replacement involves dropping of the fuel tank, removal and disposal of gasoline, and cleaning of the tank. The cleaning of the tank is crucial so that no additional contaminants are present after the new part has been replaced. It is not uncommon for the moderate DIY mechanic to tackle the task of fuel pump replacement. A failing fuel pump may simply start with a rough starting vehicle, and can lead to you being stranded when you least expect it. There are voltage tests and pressure tests that can be performed on your vehicle to determine if your fuel pump has failed, or is in danger of failing in the near future.
ToyotaPartsDeal.com is a container for extensive collection of genuine OEM Toyota parts. The fuel pump you purchase here will fit your Toyota perfectly. We remove all concerns and anxieties about verifying the part from you, and there are professional part specialists ready to assist you with it. We will never disappoint you with the deeply discounted price, and we are proud that we make you happy. We understand that every customer wants to get the order as soon as possible, so we speed up the process time. The fuel pump will be delivered to you in a complete shape, and make your Toyota being a master again on the road.
Toyota Fuel Pump Parts Questions & Experts Answers
- Q: How to check fuel pump operation and fuel pressure in OBD I and OBD II systems on 1996 through 2002 Toyota 4Runner?A:The 1993 and 1994 V6 engines are equipped with the OBD I system, which has specific testing features and self-diagnostic capabilities not found in later models that transitioned to the OBD II self-diagnosis system after 1995. For fuel system testing, the 1994 2.4L and 2.7L engines are classified as OBD I systems due to the changeover year, featuring OBD I fuel system design but updated codes and self-diagnostic capabilities. To check fuel pump operation, turn on the ignition without starting the engine, activate the fuel pump by bridging terminals +B and FP for OBD I systems or using the ignition key for OBD II systems, listen for fuel pump noise, and then turn off the ignition. If the fuel pump does not operate, inspect the EFI 15-amp fuse, ignition switch 30-amp fuse, EFI main relay, circuit opening relay, battery voltage, and wiring. For fuel pressure checks, a special fuel pressure gauge is required, and the fuel tank cap should be removed to relieve pressure. Verify battery voltage, relieve fuel pressure, and install the gauge using a banjo fitting on the fuel rail. Measure fuel pressure at idle, checking for high or low readings, and troubleshoot accordingly. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the fuel pressure regulator to check fuel pressure with and without vacuum applied, ensuring the pressure decreases with increased vacuum. If the fuel pressure is low, check the fuel feed line and pump; if high, check for blockages in the return line. After testing, relieve fuel pressure, remove the gauge, and reattach the fuel line. For EFI main relay and circuit opening relay checks, test for battery voltage at both relays, check continuity across specified terminals, and replace any faulty relays.
- Q: How to check the operation of a fuel pump on Toyota Celica?A:To check fuel pump operation, turn the ignition switch on but do not start the engine and connect terminals +B and Fp of the fuel pump check connecter using a jumper. Check the sound of fuel returning from the control, pressure of fuel through the regulator, check the pressure in the hose from the filter. Disconnect the jumper wire and unscrew the cap of the service electrical connector, finally switch off the ignition switch. Without pressure, they should check the EFI 15-amp fuse, the ignition 7.5-amp fuse, the EFI main relay, the fuel pump and, finally, the wiring and the electrical connectors. To perform the fuel pressure check, a fuel pressure gauge with an 8m banjo fitting will be needed. Others involve using a nipple by connecting this to an 8 mm banjo fitting that fits the fuel pressure gauge hose or a makeshift adapter created by making a nut from the 8 mm bolt. You must pull the fuel tank cap, check the battery voltage for being 12 or more, take out negative battery terminal, and disconnect the electrical connection of the cold start injector. Position a can underneath the cold start injector pipe banjo bolt then remove the banjo bolt and connect the fuel pressure gauge. Any dripping gasoline should be wiped off, the negative terminal of the battery reconnected, the transaxle shifted into Neutral or Park and the parking brake engaged. Connect +B and Fp of the check electrical connector, switch on the ignition and check the fuel pressure at idle on the gauge against the recommended pressure. If the system shows high pressure, then search for a restricted fuel return line; if the pressure is low, then pinch the fuel return line and observe if there is a rise in pressure. Once the jumper wire is disconnected, turn the engine on, then unscrew the vacuum sensing hose from the fuel pressure regulator, check the fuel pressure when the engine is idling, then reconnect the hose back. Ensure the fuel pressure is at the onset of 21 psi or above steady for five minutes after shutting down the engine. Remove a negative battery terminal, unscrew the fuel rail pressure test connector slowly, reattach the cold start pipe banjo connector along with new crush washers, rejoin the electrical connection to the cold start injector, and for any spilt gasoline, wipe clean. Last but not the least attach the negative battery cable and then take the car for drive to see that whether there is any leakage or not.
- Q: What are the general checks and procedures for testing a fuel pump and its electrical circuit on Toyota Sienna?A:Start with having enough fuel with you and confirming that the fuel pump is working through turning the key to ON, its hard whining sound indicates that the system is being pressurized. If there is no sound at all, then, the electrical circuit of the fuel pump should be checked. To perform a fuel pressure test get the fuel pressure gauge and the fuel injection system associated adapter. This is followed by relieving the pressurization in the fuel system, removing the outlet line from the filter and fixing the gauge. Replace the circuit opening relay, attach the battery negative terminal, insert the ignition key and watch the gauge as the pump comes on, and stays on for approximately two seconds. The pressure should ideally remain constant after the pump has ceased to work and it should not fall below the minimum even after 5 minutes. Turn the engine on and revolve it; the pressure should not change. If the pressure is not within specifications, see if it is too high or too low, replacing the fuel pressure regulator if that is an issue, and examine the fuel filter, lines, and injectors for any problems. Following the testing, reduce the pressure of fuel and take out the gauge. If the pump does not activate, check the IGN and EFI fuses, replace any of them which is fused, there may be shorts in the circuit. If the pump is still not running, look into the battery voltage of the EFI main relay and the fuel pump relay to see if the needed voltage is there. If the relays are good, but the pump will not, look for voltage at the fuel pump connector and out to ground. For relay checks, u remove the relay and use Ohm meter to check continuity between the terminals; if any, it should be replaced-as should be the case if it does not demonstrate continuity when voltage greater than battery voltage is connected to it.
Related Toyota Parts
Browse by Model
4Runner Fuel Pump 86 Fuel Pump Avalon Fuel Pump C-HR Fuel Pump Camry Fuel Pump Celica Fuel Pump Corolla Cross Fuel Pump Corolla Fuel Pump Corolla iM Fuel Pump Corona Fuel Pump Cressida Fuel Pump Crown Fuel Pump Echo Fuel Pump FJ Cruiser Fuel Pump GR Corolla Fuel Pump GR Supra Fuel Pump GR86 Fuel Pump Grand Highlander Fuel Pump Highlander Fuel Pump Land Cruiser Fuel Pump MR2 Fuel Pump MR2 Spyder Fuel Pump Matrix Fuel Pump Paseo Fuel Pump Pickup Fuel Pump Previa Fuel Pump Prius AWD-e Fuel Pump Prius C Fuel Pump Prius Fuel Pump Prius Prime Fuel Pump Prius V Fuel Pump RAV4 Fuel Pump RAV4 Prime Fuel Pump Sequoia Fuel Pump Sienna Fuel Pump Solara Fuel Pump Starlet Fuel Pump Supra Fuel Pump T100 Fuel Pump Tacoma Fuel Pump Tercel Fuel Pump Tundra Fuel Pump Van Fuel Pump Venza Fuel Pump Yaris Fuel Pump Yaris iA Fuel Pump